Aluminum: Powering the Next Era of Industrial and Green Growth
As the global economy transitions toward decarbonization, digitalization, and infrastructure renewal, aluminum has emerged as one of the most strategic industrial metals of the 21st century. Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and infinitely recyclable, aluminum continues to anchor global manufacturing, from mobility and construction to packaging and energy systems.
Global Demand Landscape

Global aluminum demand is projected to maintain a steady upward trajectory through 2025 and 2026, driven by robust expansion in transportation, construction, electrical, machinery, packaging, and consumer goods sectors. The transition to low-carbon technologies, particularly electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy infrastructure, and sustainable packaging, is transforming both the volume and nature of aluminum consumption.
Aluminum Transport Demand Dynamics
Transport Sector: The Mobility Transformation
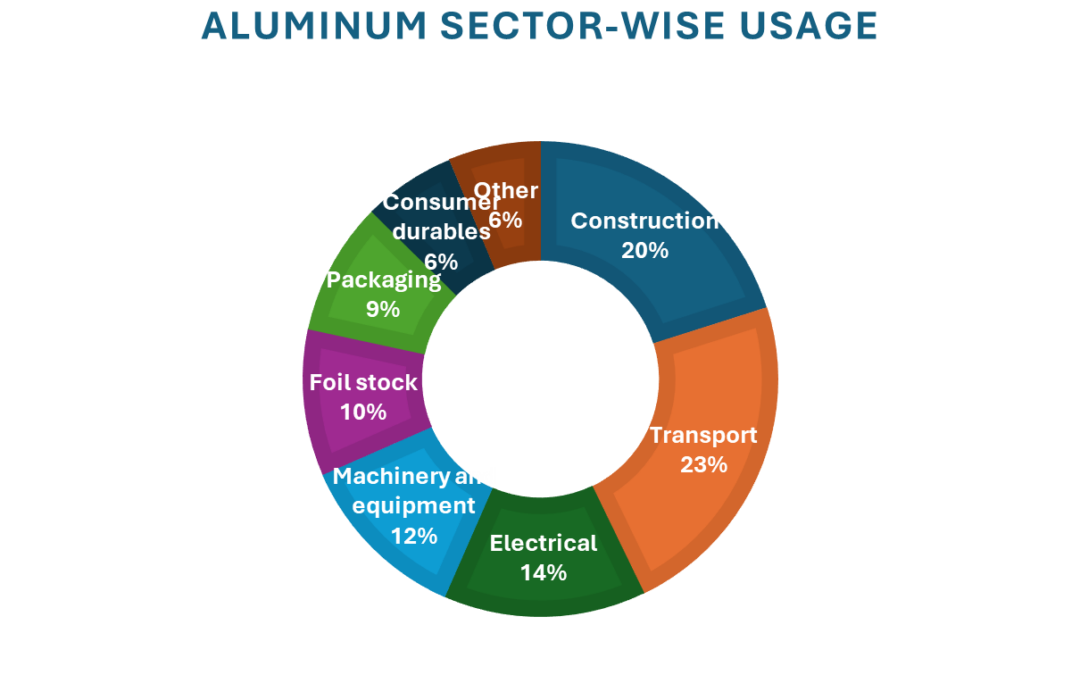
The transport sector remains aluminum’s largest end-use market, accounting for nearly a quarter of total demand. The metal’s high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and recyclability make it indispensable in vehicle manufacturing, whether for body panels, chassis, or battery enclosures.
a. Accelerating Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- EV-related aluminum demand is surging as automakers seek to offset the added weight of batteries with lighter materials, with an average of 203 kg of aluminum used per EV compared to 160 kg in conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
- Automakers in China, Europe, and the U.S. are expanding aluminum-intensive EV platforms to enhance energy efficiency and range.
- With global EV sales expected to rise sharply through 2026, aluminum intensity per vehicle is projected to increase.
This shift marks aluminum as a critical enabler of electrification, both for emissions reduction and performance optimization.

b. Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles: Sustained but Evolving Demand
While ICE vehicle production faces long-term decline, the segment continues to consume significant aluminum volumes.
- Lightweighting for fuel efficiency and emission compliance keeps demand steady in engine blocks, transmissions, and wheels.
- Developing economies, especially in South and Southeast Asia, remain key demand centers as vehicle ownership expands.
- However, the share of aluminum use in ICE vehicles is expected to phase out as EV adoption accelerates globally.
Apart from the transport sector, aluminum demand is also being driven by construction, electrical, machinery, packaging, and consumer goods industries. The building and construction sector continues to expand with urbanization and stricter green-building norms. In the electrical and power industries, the global shift toward renewables and grid modernization is driving increased aluminum use in transmission and energy systems. The packaging sector remains strong as recyclability and circular economic goals drive demand for cans and foils. Meanwhile, consumer goods and machinery rely on aluminum’s light weight and durability for modern, efficient designs.
For deeper insights and analysis, follow TransGraph.